Galandféregpetéket találtak az emberi agyban. Az alulsült szalonna lehet a hibás – Nemzeti

Galandféregpetéket találtak az emberi agyban. Az alulsült szalonna lehet a
Meglepő meglepetés érte egy 52 éves amerikai férfit, miután súlyosbodó migrén miatt kórházba került – azt mondták neki, hogy az agyában élősködő galandféreg lárvák okozták.
Az American Journal of Case Reports március 7-én megjelent esettanulmánya szerint az ismeretlen férfi négy hónapon át tartó, agresszív fejfájásra panaszkodott. Tünetei súlyosbodó súlyossága miatt CT-vizsgálatra kórházba szállították.
A vizsgálatok több cisztát is kimutattak az agyában. Számos vizsgálat után az orvosok megtalálták állapotának okát: parazita galandféreg lárvákat, amelyekről ismert, hogy neurocysticercosis-t, az agy ritka és veszélyes fertőzését okozzák.
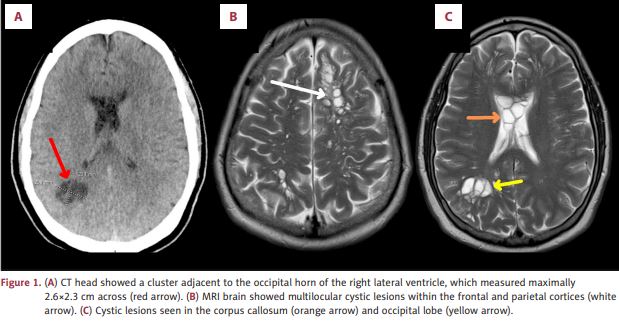
Neurocysticercosis is a condition caused by parasitic tapeworms when cysts embed within the nervous system, according to the study. These parasites may be located anywhere from brain parenchyma to the ventricular system and spinal cord.
American Journal of Case Reports
Neurocysticercosis is the most common parasitic disease of the central nervous system and is linked to accidental ingestion of pork tapeworm eggs, according to the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ). It causes about 50,000 deaths per year and is the leading cause of epilepsy worldwide.
The CMAJ added that the prevalence of infection is increasing in developed countries as more people travel to or migrate from regions where infection is endemic. The disease remains prevalent in Asia, Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in developing countries and areas where pigs are raised as primary food sources.
The patient’s medical team tried to find the origin of the parasitic larvae infesting his brain. According to the study, the man had not recently traveled to any high-risk areas. His only notable travel history was a cruise to the Bahamas two years prior. Further, he “denied any food insecurity,” researchers said, adding the man lived with his wife and cat in a modern home.
The latest health and medical news
emailed to you every Sunday.
The latest health and medical news
emailed to you every Sunday.
On further questioning, the man also denied eating raw food but “admitted to a habit of eating lightly cooked, non-crispy bacon for most of his life,” the study said.
“Our patient’s lifelong preference for soft bacon may have led to instances of undercooked bacon consumption,” the researchers said.
However, they said eating undercooked bacon would have caused him to develop taeniasis, an intestinal tapeworm, and not cysticercosis in his brain.
“It can only be speculated, but given our patient’s predilection for undercooked pork and benign exposure history, we favor that his cysticercosis was transmitted via autoinfection after improper handwashing after he had contracted taeniasis himself from his eating habits,” they said.
Following treatment with anti-parasitic and anti-inflammatory medications, the patient experienced significant improvement in his condition, the study said. Notably, the brain lesions regressed and his migraines improved.
“It is historically very unusual to encounter infected pork in the United States, and our case may have public health implications,” the researchers concluded.
© 2024 Global News, a division of Corus Entertainment Inc.








